The idea behind Gas Tokens is simple. When the network is quiet and the fee is low, get gas tokens and use it when the network is busy and the fee is high.
In a way, it can be said that with the help of these tokens, which are created in different networks, the network gas is tokenized. In this article, we want to see in more detail what the gas token is and how it works.
We also take a look at the recent gas token scam related to multichain access revocation.
Key points of Gas token
- The idea of gas tokens is to mint them when the gas price is low and use them when the fee is high.
- CHI, GST1 and GST2 tokens are famous gas tokens.
- Gas tokens were created due to the Storage Fund feature in networks. The purpose of this feature was to encourage developers to clean up unnecessary data and contracts from the network.
- Ethereum removed the Storage Fund feature in 2021 due to the problems caused by gas tokens.
In this article we will cover:
- What is Gas Token?
- How does Gas Token work?
- How is it beneficial to use gas token?
- The case of Gas Tokens fraud in Multichain hack
- Frequently asked questions on gas token
What is Gas Token?
In order to better understand what Gas Token is, we must first have some information about Gas. In a network like Ethereum and other similar networks, Gas is the fuel that must be paid by the user for processing transactions and allocating computing resources from the network side.
A certain amount of gas must be paid for each job, and the higher the complexity of the transaction, the higher the amount of gas paid.
For example, in the Ethereum network, the simplest transaction is the transfer of ether between two addresses, for which the lowest amount of gas is paid.
On the other hand, to create complex smart contracts, the largest amount of gas must be paid. The amount we pay as a fee in the form of Ether is the product of gas used and gas price (gasUsed * gasPrice).
Gas is taken because malicious codes do not reduce the processing power of the network. In fact, this cost both prevents malicious behavior and can be an incentive for developers to write their code optimally.
You probably know that when the network is busy, the price of gas increases, and in a quiet network, transactions can be done at a much lower cost.
As we said, the idea of gas tokens is simple and the purpose of their presentation was to mint or buy Gas Token when the network is quiet and to pay for our transaction when the network is busy.
One of the famous gas tokens was CHI, which was developed by the 1Inch team. Among other gas tokens, GST1 and GST2 can be mentioned.
But the important thing you should know is that the ethereum network, as the birthplace of gas tokens, removed this feature in 2021. The reason for this action was that the destructive effects of these tokens on the network were greater than their benefits. But this feature is still available in other networks such as BSC.
How does Gas Token work?
In this section, we want to explain how GAS Token works in simple language and away from technical complications. In order to understand how gas token works, it is better to know about Gas Refund and Storage Refund in Ethereum network.
Sometimes it happens that the execution of a transaction in the network consumes less than the usual amount of gas. Naturally, this situation does not occur during the execution of the simplest type of transaction that consumes the least amount of gas.
For example, you want to make a complex transaction, but for some reason, the request fails before processing. In this case, the gas consumed is less than the amount paid, and the remaining amount of gas is returned to the address of the sender of the transaction.
This is the concept of Gas Refund in the Ethereum network, which is also fair.
The second concept we want to address is Storage Refund. As you know, smart contracts create data on the network and this data is always stored on the blockchain.
In order to encourage developers to store less data on the network and delete information they don’t need, Ethereum introduced Storage Refund, which can be considered a subset of Gas Refund.
There were two functions or functions SSTORE and SELFDESTRUCT for the same Storage Refund discussion in Ethereum, the first one by deleting the stored data and the second one by destroying the smart contract, causing gas refund.
So there can be two gas token models. In the first type, with the Gas Token mint, more data is included in the smart contract of the token, and at the time of burning, by erasing the data, a certain amount of gas is refunded.
In the second model, a smart contract is created with the mint gas token, and when the gas token is burned, the smart contract is destroyed, which is the result of gas refund.
How is it beneficial to use gas token?
When we use gas tokens, we pay an amount of gas for minting the token (at the price of gas at the time of minting) and an amount of gas for burning the token (at the price of gas at the time of burning).
But in exchange for burning the token, the amount of gas (at the price of gas at the time of burning) is refunded.
Using gas tokens is beneficial for us when the price of gas at the time of burning has a significant difference with the price of gas at the time of minting.
That is, when the network is quiet, mint the token with a low gas price, and burn the token when the network is busy with a high gas price.
In this case, although we pay more gas, the ether received due to the product of the refunded gas in the daily price of gas creates a profit for us.
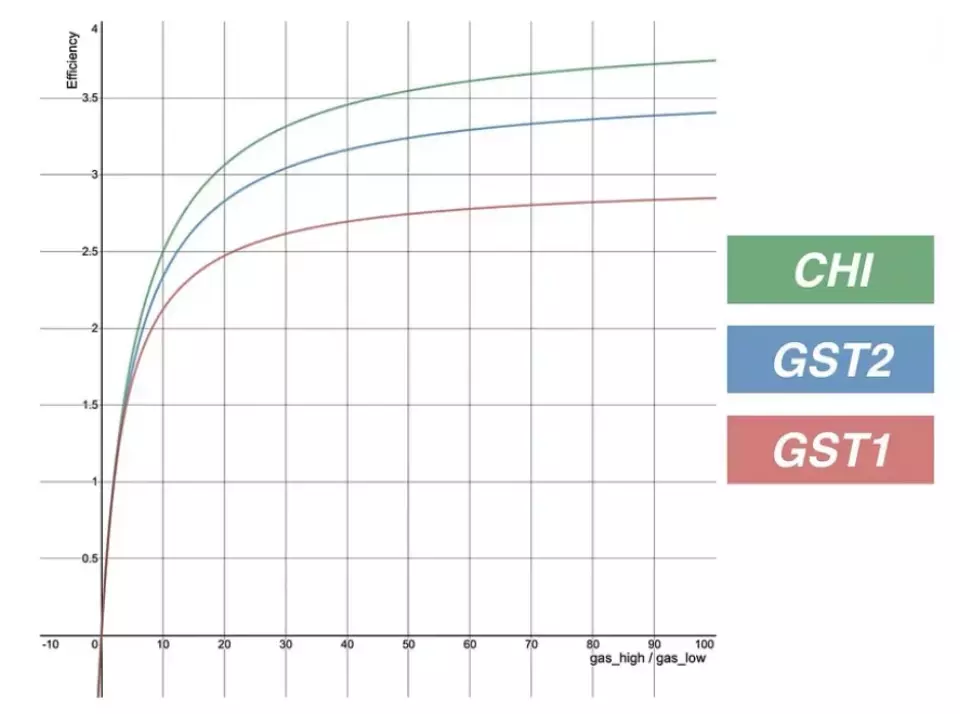
The above curve was prepared by the 1Inch team and shows the gas efficiency of various tokens in terms of the ratio of the gas price at the time of burning to the gas price at the time of minting.
The case of Gas Tokens fraud in Multichain hack
One of the most popular news of this month was the exploit attack on Multichain Bridge on July 7, during which 126 million dollars were stolen.
It was after this attack that different platforms and security tools asked users to revoke the access of the smart contracts of this protocol to their wallets as soon as possible and in order to prevent the theft of their assets.
A hacker saw the excitement and influx of users to cancel access as a good opportunity for fraud, and for this purpose, he used the gas token on the BSC network. As we said, the Storage Refund feature was not lost in the BSC network, unlike Ethereum.
He created fake tokens with well-known token names like Dai (no logo) with fake accesses and airdropped these tokens to many wallets.
From this link, you can see the token smart contract in Bsc scan. Users in a hurry did not notice this fake token in their wallet and immediately proceeded to Revoke all access to their wallet.
These tokens were coded in such a way that when access was revoked, it minted the full capacity of the CHI token block gas and sent it to the address of the smart contract maker of the token.
Users did not notice this and paid a large amount of BNB as a fee (about 100 times normal) to cancel access to these tokens. In one case, the user paid a fee equivalent to 60 BNB dollars to cancel access.
This hacker can eventually get a significant amount of BNB from gas refunds by burning CHI tokens. Of course, after this issue became clear, platforms like Rabby and Revoke Cash started working and if the access cancellation fee was too high, they would stop it.
In addition, they also informed about this matter on Twitter.
Frequently asked questions on gas token
What is Gas Token?
Gas tokens were created with the idea of managing transaction fees. In this way, the user mints these tokens when it is quiet and the price of network gas is low, and uses them when it is crowded and the price of network gas is high.
In which networks are there gas tokens?
Gas Token was created first on the Ethereum network and then on similar networks. In 2021, Ethereum removed this feature because of the problems it caused. But this feature still exists in networks like BSC, and it becomes problematic in times like this Multichain bridge hack.
One of the things for which new solutions are still being developed is the problem of high transaction fees when blockchain networks, including Ethereum, are crowded.
One of the solutions to overcome this issue was the idea of gas tokens, in such a way that the user mints these tokens when the network is quiet and receives a reward for burning these tokens and removing data from the network when the network is busy.
An idea that, despite its advantages, caused many problems and was finally removed from Ethereum.
In this article, we discussed what Gas Token is and explained its working mechanism. We also mentioned the recent fraud with the help of gas tokens in the BSC network.
What do you think about this idea? Have you had the experience of using Gas Token?


